How to Upload Image Template to Docs
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to have advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Prepare a Windows VHD or VHDX to upload to Azure
Applies to: ✔️ Windows VMs
Before you upload a Windows virtual machine (VM) from on-premises to Azure, yous must prepare the virtual hard disk drive (VHD or VHDX). Azure supports both generation 1 and generation ii VMs that are in VHD file format and that accept a fixed-size disk. The maximum size immune for the OS VHD on a generation 1 VM is two TB.
You can convert a VHDX file to VHD, convert a dynamically expanding disk to a fixed-size disk, but you can't change a VM's generation. For more information, see Should I create a generation one or 2 VM in Hyper-5? and Support for generation 2 VMs on Azure.
For information nearly the back up policy for Azure VMs, see Microsoft server software support for Azure VMs.
Note
The instructions in this article apply to:
- The 64-chip version of Windows Server 2008 R2 and after Windows Server operating systems. For data nigh running a 32-scrap operating system in Azure, see Support for 32-chip operating systems in Azure VMs.
- If any Disaster Recovery tool will be used to drift the workload, like Azure Site Recovery or Azure Migrate, this process is still required on the Guest Bone to prepare the image before the migration.
System File Checker
Run Windows System File Checker utility before generalization of OS paradigm
The Arrangement File Checker (SFC) is used to verify and replace Windows arrangement files.
Important
Apply an elevated PowerShell session to run the examples in this article.
Run the SFC command:
sfc.exe /scannow Outset system scan. This process will take some time. Beginning verification phase of organisation scan. Verification 100% complete. Windows Resource Protection did not observe whatever integrity violations. After the SFC browse completes, install Windows Updates and restart the computer.
Set Windows configurations for Azure
Note
Azure platform mounts an ISO file to the DVD-ROM when a Windows VM is created from a generalized prototype. For this reason, the DVD-ROM must exist enabled in the OS in the generalized epitome. If it is disabled, the Windows VM volition be stuck at out-of-box feel (OOBE).
-
Remove whatever static persistent routes in the routing tabular array:
- To view the routing tabular array, run
route.exe print. - Check the Persistence Routes section. If there'southward a persistent route, utilise the
route.exe deletecontrol to remove it.
- To view the routing tabular array, run
-
Remove the WinHTTP proxy:
netsh.exe winhttp reset proxyIf the VM needs to work with a specific proxy, add a proxy exception for the Azure IP address (168.63.129.16) so the VM can connect to Azure:
$proxyAddress='<your proxy server>' $proxyBypassList='<your list of bypasses>;168.63.129.16' netsh.exe winhttp set proxy $proxyAddress $proxyBypassList -
Open DiskPart:
diskpart.exeSet the disk SAN policy to
Onlineall:DISKPART> san policy=onlineall DISKPART> exit -
Set up Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) fourth dimension for Windows. Also, set the startup type of the Windows time service w32time to Automatic:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Organisation\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation -Proper noun RealTimeIsUniversal -Value 1 -Type DWord -Force Set-Service -Name w32time -StartupType Automatic -
Set the power profile to high performance:
powercfg.exe /setactive SCHEME_MIN -
Brand sure the ecology variables TEMP and TMP are set to their default values:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Director\Environment' -Name TEMP -Value "%SystemRoot%\TEMP" -Type ExpandString -Force Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Command\Session Manager\Environment' -Proper noun TMP -Value "%SystemRoot%\TEMP" -Type ExpandString -Strength -
For VMs with legacy operating systems (Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows 8.1 and below), make certain the latest Hyper-V Integration Component Services are installed. For more information, run into Hyper-V integration components update for Windows VM.
Annotation
In a scenario where VMs are to be ready up with a disaster recovery solution between the on-premise VMware server and Azure, the Hyper-5 Integration Component Services tin't be used. If that'southward the case, please contact the VMware support to drift the VM to Azure and make it co-reside in VMware server.
Check the Windows services
Make certain that each of the post-obit Windows services is set to the Windows default value. These services are the minimum that must be configured to ensure VM connectivity. To set the startup settings, run the post-obit example:
Get-Service -Name BFE, Dhcp, Dnscache, IKEEXT, iphlpsvc, nsi, mpssvc, RemoteRegistry | Where-Object StartType -ne Automatic | Fix-Service -StartupType Automatic Get-Service -Name Netlogon, Netman, TermService | Where-Object StartType -ne Manual | Set up-Service -StartupType Manual Update remote desktop registry settings
Brand sure the following settings are configured correctly for remote access:
Note
If you receive an fault message when running Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services -Proper name <string> -Value <object>, you can safely ignore it. It means the domain isn't setting that configuration through a Group Policy Object.
-
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is enabled:
Ready-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organization\CurrentControlSet\Control\Last Server' -Name fDenyTSConnections -Value 0 -Type DWord -Force Fix-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Concluding Services' -Proper name fDenyTSConnections -Value 0 -Type DWord -Strength -
The RDP port is ready correctly using the default port of 3389:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organisation\CurrentControlSet\Command\Terminal Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Name PortNumber -Value 3389 -Type DWord -ForceWhen y'all deploy a VM, the default rules are created for port 3389. To change the port number, do that after the VM is deployed in Azure.
-
The listener is listening on every network interface:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Command\Terminal Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Name LanAdapter -Value 0 -Type DWord -Force -
Configure network-level authentication (NLA) fashion for the RDP connections:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Last Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -Name UserAuthentication -Value ane -Blazon DWord -Force -
Ready the keep-live value:
Prepare-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Concluding Services' -Name KeepAliveEnable -Value 1 -Type DWord -Force Fix-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Concluding Services' -Name KeepAliveInterval -Value ane -Type DWord -Force Fix-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organization\CurrentControlSet\Control\Concluding Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Proper name KeepAliveTimeout -Value one -Type DWord -Forcefulness -
Set the reconnect options:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Last Services' -Name fDisableAutoReconnect -Value 0 -Type DWord -Force Fix-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Proper noun fInheritReconnectSame -Value 1 -Type DWord -Force Fix-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organization\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Proper name fReconnectSame -Value 0 -Type DWord -Force -
Limit the number of concurrent connections:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organization\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\Winstations\RDP-Tcp' -Proper noun MaxInstanceCount -Value 4294967295 -Type DWord -Force -
Remove any self-signed certificates tied to the RDP listener:
if ((Get-Item -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp').Holding -contains 'SSLCertificateSHA1Hash') { Remove-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -Name SSLCertificateSHA1Hash -Force }This code ensures that y'all tin can connect when you deploy the VM. You can too review these settings after the VM is deployed in Azure.
-
If the VM is part of a domain, check the following policies to make sure the previous settings aren't reverted.
Goal Policy Value RDP is enabled Calculator Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections Let users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop NLA group policy Settings\Administrative Templates\Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Security Require user hallmark for remote admission by using NLA Keep-alive settings Estimator Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections Configure keep-alive connexion interval Reconnect settings Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections Reconnect automatically Limited number of connectedness settings Figurer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Authoritative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections Limit number of connections
Configure Windows Firewall rules
-
Turn on Windows Firewall on the 3 profiles (domain, standard, and public):
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain, Public, Private -Enabled True -
Run the following instance to allow WinRM through the iii firewall profiles (domain, private, and public), and enable the PowerShell remote service:
Enable-PSRemoting -Force Set-NetFirewallRule -Name WINRM-HTTP-In-TCP, WINRM-HTTP-In-TCP-PUBLIC -Enabled True -
Enable the following firewall rules to let the RDP traffic:
Set-NetFirewallRule -Group '@FirewallAPI.dll,-28752' -Enabled True -
Enable the rule for file and printer sharing so the VM can respond to ping requests inside the virtual network:
Ready-NetFirewallRule -Proper name FPS-ICMP4-ERQ-In -Enabled True -
Create a rule for the Azure platform network:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName AzurePlatform -Direction Inbound -RemoteAddress 168.63.129.16 -Contour Whatsoever -Action Allow -EdgeTraversalPolicy Let New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName AzurePlatform -Direction Outbound -RemoteAddress 168.63.129.xvi -Profile Whatsoever -Activeness Permit -
If the VM is part of a domain, check the post-obit Azure Advertisement policies to make sure the previous settings aren't reverted.
Goal Policy Value Enable the Windows Firewall profiles Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Network\Network Connectedness\Windows Firewall\Domain Profile\Windows Firewall Protect all network connections Enable RDP Calculator Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Network\Network Connectedness\Windows Firewall\Domain Profile\Windows Firewall Allow inbound Remote Desktop exceptions Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Authoritative Templates\Network\Network Connection\Windows Firewall\Standard Profile\Windows Firewall Allow inbound Remote Desktop exceptions Enable ICMP-V4 Calculator Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Network\Network Connection\Windows Firewall\Domain Profile\Windows Firewall Permit ICMP exceptions Reckoner Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Administrative Templates\Network\Network Connectedness\Windows Firewall\Standard Profile\Windows Firewall Allow ICMP exceptions
Verify the VM
Make sure the VM is healthy, secure, and RDP accessible:
-
To brand sure the disk is healthy and consequent, check the disk at the side by side VM restart:
chkdsk.exe /fMake sure the report shows a clean and healthy disk.
-
Gear up the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) settings.
cmd bcdedit.exe /set "{bootmgr}" integrityservices enable bcdedit.exe /prepare "{default}" device sectionalisation=C: bcdedit.exe /set up "{default}" integrityservices enable bcdedit.exe /set "{default}" recoveryenabled Off bcdedit.exe /set "{default}" osdevice partition=C: bcdedit.exe /set "{default}" bootstatuspolicy IgnoreAllFailures #Enable Serial Panel Feature bcdedit.exe /set "{bootmgr}" displaybootmenu yes bcdedit.exe /set up "{bootmgr}" timeout five bcdedit.exe /set "{bootmgr}" bootems yeah bcdedit.exe /ems "{electric current}" ON bcdedit.exe /emssettings EMSPORT:i EMSBAUDRATE:115200 exit -
The dump log tin be helpful in troubleshooting Windows crash bug. Enable the dump log collection:
# Gear up the invitee OS to collect a kernel dump on an Os crash event Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Organisation\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl' -Proper name CrashDumpEnabled -Type DWord -Strength -Value 2 Gear up-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Arrangement\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl' -Proper noun DumpFile -Type ExpandString -Force -Value "%SystemRoot%\Retentivity.DMP" Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Arrangement\CurrentControlSet\Command\CrashControl' -Proper noun NMICrashDump -Type DWord -Forcefulness -Value ane # Fix upwards the guest OS to collect user mode dumps on a service crash event $central = 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting\LocalDumps' if ((Test-Path -Path $primal) -eq $false) {(New-Detail -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting' -Proper noun LocalDumps)} New-ItemProperty -Path $cardinal -Name DumpFolder -Type ExpandString -Forcefulness -Value 'C:\CrashDumps' New-ItemProperty -Path $primal -Proper noun CrashCount -Blazon DWord -Strength -Value 10 New-ItemProperty -Path $key -Name DumpType -Blazon DWord -Force -Value ii Gear up-Service -Proper name WerSvc -StartupType Manual -
Verify that the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) repository is consistent:
winmgmt.exe /verifyrepositoryIf the repository is corrupted, see WMI: Repository corruption or not.
-
Make certain no other applications than TermService are using port 3389. This port is used for the RDP service in Azure. To run into which ports are used on the VM, run
netstat.exe -anob:netstat.exe -anobThe post-obit is an example.
netstat.exe -anob | findstr 3389 TCP 0.0.0.0:3389 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4056 TCP [::]:3389 [::]:0 LISTENING 4056 UDP 0.0.0.0:3389 *:* 4056 UDP [::]:3389 *:* 4056 tasklist /svc | findstr 4056 svchost.exe 4056 TermService -
To upload a Windows VHD that's a domain controller:
-
Follow these extra steps to gear up the disk.
-
Make sure you know the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) password in case you ever accept to start the VM in DSRM. For more than information, meet Set a DSRM password.
-
-
Make sure you know the built-in administrator account and password. You might want to reset the current local administrator password and brand sure you tin use this account to sign in to Windows through the RDP connectedness. This access permission is controlled by the "Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services" Group Policy Object. View this object in the Local Group Policy Editor:
-
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Consignment
-
-
Cheque the following Azure Advertizement policies to make sure they're not blocking RDP access:
-
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Consignment\Deny admission to this calculator from the network -
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Deny log on through Remote Desktop Services
-
-
Check the following Azure Advertising policy to make sure they're not removing any of the required access accounts:
-
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment\Access this computer from the network
The policy should list the following groups:
-
Administrators
-
Backup Operators
-
Everyone
-
Users
-
-
Restart the VM to make sure that Windows is still salubrious and can exist reached through the RDP connection. At this betoken, consider creating a VM on your local Hyper-V server to brand sure the VM starts completely. So examination to make sure y'all tin reach the VM through RDP.
-
Remove whatsoever extra Ship Driver Interface (TDI) filters. For case, remove software that analyzes TCP packets or extra firewalls.
-
Uninstall any other third-party software or driver that's related to physical components or any other virtualization technology.
Install Windows updates
Note
If you lot also need to practise a generalization of the OS (sysprep), y'all must update Windows and restart the VM before running the Sysprep control.
Ideally, you should keep the car updated to the patch level, if this isn't possible, make sure the following updates are installed. To get the latest updates, see the Windows update history pages: Windows 10, and Windows Server 2019, Windows viii.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows vii SP1, and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1.
| Component | Binary | Windows 7 SP1, Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | Windows 8, Windows Server 2012 | Windows eight.ane, Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows x v1607, Windows Server 2016 v1607 | Windows x v1703 | Windows ten v1709, Windows Server 2016 v1709 | Windows x v1803, Windows Server 2016 v1803 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | disk.sys | 6.i.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | six.2.9200.17638 / six.two.9200.21757 - KB3137061 | 6.3.9600.18203 - KB3137061 | - | - | - | - |
| storport.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | half-dozen.2.9200.17188 / half dozen.ii.9200.21306 - KB3018489 | half dozen.iii.9600.18573 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1358 - KB4022715 | x.0.15063.332 | - | - | |
| ntfs.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | 6.2.9200.17623 / 6.2.9200.21743 - KB3121255 | six.three.9600.18654 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1198 - KB4022715 | ten.0.15063.447 | - | - | |
| Iologmsg.dll | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | 6.2.9200.16384 - KB2995387 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Classpnp.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | half dozen.2.9200.17061 / half dozen.2.9200.21180 - KB2995387 | 6.3.9600.18334 - KB3172614 | 10.0.14393.953 - KB4022715 | - | - | - | |
| Volsnap.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | half dozen.two.9200.17047 / six.2.9200.21165 - KB2975331 | 6.3.9600.18265 - KB3145384 | - | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - | |
| partmgr.sys | half dozen.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | 6.2.9200.16681 - KB2877114 | 6.three.9600.17401 - KB3000850 | 10.0.14393.953 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - | |
| volmgr.sys | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - | |||||
| Volmgrx.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | - | - | - | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - | |
| Msiscsi.sys | half dozen.i.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | half-dozen.2.9200.21006 - KB2955163 | 6.3.9600.18624 - KB4022726 | ten.0.14393.1066 - KB4022715 | ten.0.15063.447 | - | - | |
| Msdsm.sys | half dozen.one.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | vi.ii.9200.21474 - KB3046101 | 6.three.9600.18592 - KB4022726 | - | - | - | - | |
| Mpio.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | 6.2.9200.21190 - KB3046101 | 6.3.9600.18616 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1198 - KB4022715 | - | - | - | |
| vmstorfl.sys | six.3.9600.18907 - KB4072650 | 6.three.9600.18080 - KB3063109 | 6.three.9600.18907 - KB4072650 | x.0.14393.2007 - KB4345418 | ten.0.15063.850 - KB4345419 | 10.0.16299.371 - KB4345420 | - | |
| Fveapi.dll | vi.1.7601.23311 - KB3125574 | 6.ii.9200.20930 - KB2930244 | half-dozen.3.9600.18294 - KB3172614 | x.0.14393.576 - KB4022715 | - | - | - | |
| Fveapibase.dll | 6.one.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | 6.2.9200.20930 - KB2930244 | half dozen.3.9600.17415 - KB3172614 | ten.0.14393.206 - KB4022715 | - | - | - | |
| Network | netvsc.sys | - | - | - | 10.0.14393.1198 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.250 - KB4020001 | - | - |
| mrxsmb10.sys | 6.1.7601.23816 - KB4022722 | 6.ii.9200.22108 - KB4022724 | six.3.9600.18603 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.479 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.483 | - | - | |
| mrxsmb20.sys | 6.1.7601.23816 - KB4022722 | 6.2.9200.21548 - KB4022724 | 6.3.9600.18586 - KB4022726 | x.0.14393.953 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.483 | - | - | |
| mrxsmb.sys | 6.ane.7601.23816 - KB4022722 | half dozen.ii.9200.22074 - KB4022724 | 6.three.9600.18586 - KB4022726 | ten.0.14393.953 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - | |
| tcpip.sys | vi.1.7601.23761 - KB4022722 | half dozen.2.9200.22070 - KB4022724 | 6.three.9600.18478 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1358 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.447 | - | - | |
| http.sys | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | half dozen.2.9200.17285 - KB3042553 | 6.iii.9600.18574 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.251 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.483 | - | - | |
| vmswitch.sys | 6.one.7601.23727 - KB4022719 | 6.2.9200.22117 - KB4022724 | vi.3.9600.18654 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1358 - KB4022715 | ten.0.15063.138 | - | - | |
| Core | ntoskrnl.exe | 6.1.7601.23807 - KB4022719 | 6.2.9200.22170 - KB4022718 | 6.3.9600.18696 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1358 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.483 | - | - |
| Remote Desktop Services | rdpcorets.dll | 6.2.9200.21506 - KB4022719 | six.2.9200.22104 - KB4022724 | half-dozen.iii.9600.18619 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.1198 - KB4022715 | 10.0.15063.0 | - | - |
| termsrv.dll | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | six.ii.9200.17048 - KB2973501 | half dozen.three.9600.17415 - KB3000850 | 10.0.14393.0 - KB4022715 | ten.0.15063.0 | - | - | |
| termdd.sys | 6.i.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| win32k.sys | six.1.7601.23807 - KB4022719 | 6.2.9200.22168 - KB4022718 | 6.3.9600.18698 - KB4022726 | 10.0.14393.594 - KB4022715 | - | - | - | |
| rdpdd.dll | 6.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| rdpwd.sys | half-dozen.1.7601.23403 - KB3125574 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Security | MS17-010 | KB4012212 | KB4012213 | KB4012213 | KB4012606 | KB4012606 | - | - |
| KB4012216 | KB4013198 | KB4013198 | - | - | ||||
| KB4012215 | KB4012214 | KB4012216 | KB4013429 | KB4013429 | - | - | ||
| KB4012217 | KB4013429 | KB4013429 | - | - | ||||
| CVE-2018-0886 | KB4103718 | KB4103730 | KB4103725 | KB4103723 | KB4103731 | KB4103727 | KB4103721 | |
| KB4103712 | KB4103726 | KB4103715 |
Notation
To avoid an accidental reboot during VM provisioning, nosotros recommend ensuring that all Windows Update installations are finished and that no updates are pending. One way to do this is to install all possible Windows updates and reboot once before you run the sysprep.exe command.
Determine when to use Sysprep
Arrangement Preparation Tool (sysprep.exe) is a procedure you lot tin run to reset a Windows installation. Sysprep provides an "out of the box" experience by removing all personal data and resetting several components.
You typically run sysprep.exe to create a template from which you can deploy several other VMs that have a specific configuration. The template is called a generalized image.
To create only one VM from ane disk, y'all don't have to use Sysprep. Instead, you tin can create the VM from a specialized image. For information about how to create a VM from a specialized disk, see:
- Create a VM from a specialized disk
- Create a VM from a specialized VHD deejay
To create a generalized image, yous need to run Sysprep. For more information, see How to use Sysprep: An introduction.
Non every role or application that's installed on a Windows-based calculator supports generalized images. Before you use this process, make sure Sysprep supports the office of the computer. For more data, come across Sysprep support for server roles.
In particular, Sysprep requires the drives to exist fully decrypted earlier execution. If you have enabled encryption on your VM, disable it before running Sysprep.
Generalize a VHD
Annotation
If you're creating a generalized image from an existing Azure VM, we recommend to remove the VM extensions before running the sysprep.
Note
After you run sysprep.exe in the following steps, turn off the VM. Don't turn it back on until you create an epitome from information technology in Azure.
-
Sign in to the Windows VM.
-
Run a PowerShell session as an administrator.
-
Delete the panther directory (C:\Windows\Panther).
-
Change the directory to
%windir%\system32\sysprep. Then runsysprep.exe. -
In the System Preparation Tool dialog box, select Enter System Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE), and brand certain the Generalize checkbox is selected.
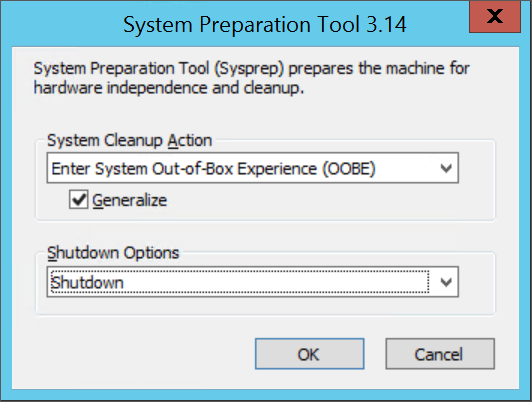
-
In Shutdown Options, select Shutdown.
-
Select OK.
-
When Sysprep finishes, shut downwardly the VM. Don't use Restart to shut down the VM.
Now the VHD is ready to be uploaded. For more information almost how to create a VM from a generalized deejay, see Upload a generalized VHD and employ it to create a new VM in Azure.
Catechumen the virtual disk to a fixed size VHD
Use one of the methods in this department to convert and resize your virtual disk to the required format for Azure:
-
Back up the VM before y'all run the virtual disk conversion or resize process.
-
Brand sure that the Windows VHD works correctly on the local server. Resolve whatsoever errors within the VM itself before you effort to convert or upload it to Azure.
-
Convert the virtual disk to type fixed.
-
Resize the virtual disk to meet Azure requirements:
-
Disks in Azure must have a virtual size aligned to ane MiB. If your VHD is a fraction of i MiB, you lot'll need to resize the disk to a multiple of ane MiB. Disks that are fractions of a MiB cause errors when creating images from the uploaded VHD. To verify the size you can utilise the PowerShell Become-VHD cmdlet to bear witness "Size", which must exist a multiple of ane MiB in Azure, and "FileSize", which will exist equal to "Size" plus 512 bytes for the VHD footer.
$vhd = Get-VHD -Path C:\test\MyNewVM.vhd $vhd.Size % 1MB 0 $vhd.FileSize - $vhd.Size 512 -
The maximum size allowed for the Os VHD with a generation i VM is 2,048 GiB (2 TiB),
-
The maximum size for a data disk is 32,767 GiB (32 TiB).
-
Annotation
- If y'all are preparing a Windows OS disk after you lot convert to a stock-still disk and resize if needed, create a VM that uses the disk. Start and sign in to the VM and keep with the sections in this article to finish preparing it for uploading.
- If yous are preparing a data disk you may stop with this section and go along to uploading your disk.
Utilise Hyper-5 Manager to convert the disk
- Open Hyper-V Manager and select your local reckoner on the left. In the carte above the figurer list, select Action > Edit Deejay.
- On the Locate Virtual Hard disk page, select your virtual disk.
- On the Choose Action page, select Convert > Side by side.
- To convert from VHDX, select VHD > Next.
- To convert from a dynamically expanding disk, select Stock-still size > Adjacent.
- Locate and select a path to salve the new VHD file.
- Select Stop.
Use PowerShell to catechumen the deejay
You tin convert a virtual disk using the Convert-VHD cmdlet in PowerShell. If you need data near installing this cmdlet meet Install the Hyper-V part.
The following example converts the disk from VHDX to VHD. It also converts the disk from a dynamically expanding disk to a fixed-size disk.
Convert-VHD -Path C:\exam\MyVM.vhdx -DestinationPath C:\exam\MyNewVM.vhd -VHDType Fixed In this example, supersede the value for Path with the path to the virtual hard disk that y'all want to convert. Supercede the value for DestinationPath with the new path and name of the converted disk.
Use Hyper-V Manager to resize the deejay
- Open Hyper-V Manager and select your local reckoner on the left. In the carte du jour above the computer list, select Action > Edit Disk.
- On the Locate Virtual Hard disk drive folio, select your virtual deejay.
- On the Choose Action page, select Expand > Next.
- On the Locate Virtual Hard Deejay page, enter the new size in GiB > Adjacent.
- Select Terminate.
Use PowerShell to resize the deejay
You lot can resize a virtual disk using the Resize-VHD cmdlet in PowerShell. If you lot need information nigh installing this cmdlet see Install the Hyper-Five role.
The following example resizes the disk from 100.5 MiB to 101 MiB to meet the Azure alignment requirement.
Resize-VHD -Path C:\test\MyNewVM.vhd -SizeBytes 105906176 In this example, replace the value for Path with the path to the virtual hard disk that you lot want to resize. Supersede the value for SizeBytes with the new size in bytes for the deejay.
Catechumen from VMware VMDK disk format
If you have a Windows VM image in the VMDK file format, so you can use Azure Migrate to convert the VMDK and upload it to Azure.
Complete the recommended configurations
The following settings don't bear upon VHD uploading. Nonetheless, we strongly recommend that you configured them.
-
Install the Azure Virtual Machine Agent. And then y'all tin can enable VM extensions. The VM extensions implement near of the critical functionality that yous might want to use with your VMs. Y'all'll demand the extensions, for example, to reset passwords or configure RDP. For more than data, see the Azure Virtual Machine Agent overview.
-
After y'all create the VM in Azure, we recommend that you put the page file on the temporal drive volume to improve performance. You can ready the file placement as follows:
Ready-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Managing director\Retentiveness Management' -Name PagingFiles -Value 'D:\pagefile.sys' -Type MultiString -ForceIf a data disk is attached to the VM, the temporal drive volume'due south letter is typically D. This designation could be different, depending on your settings and the number of available drives.
- We recommend disabling script blockers that might exist provided by antivirus software. They might interfere and block the Windows Provisioning Agent scripts executed when you lot deploy a new VM from your image.
Next steps
- Upload a Windows VM image to Azure for Resource Director deployments
- Troubleshoot Azure Windows VM activation problems
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
melansonwrintrah61.blogspot.com
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/prepare-for-upload-vhd-image
0 Response to "How to Upload Image Template to Docs"
Post a Comment